Common warning signs of brain tumors
(Dan Tri) – According to many studies, pituitary adenoma is quite common, one of the four most common intracranial tumors.
What is a pituitary tumor?
According to Viet Duc Friendship Hospital, pituitary tumor is a tumor that develops from pituitary gland cells. This is a benign, slow growing tumor. The pituitary tumor is located in the pituitary fossa (at the base of the skull just behind the base of the nose). The pituitary gland secretes many important hormones (hormones) that control many other endocrine glands in the body. Pituitary tumors are one of the four most common intracranial tumors (metastatic brain tumors, meningiomas, gliomas, and pituitary tumors).
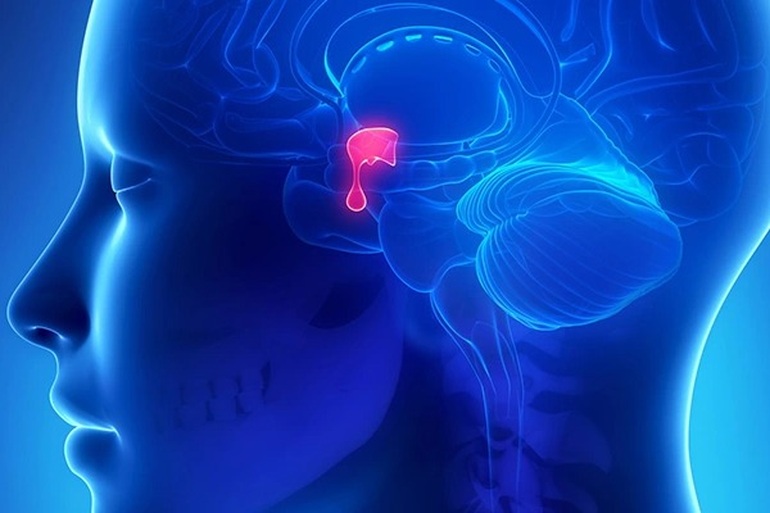
The pituitary gland has many different types of glandular cells, each of which secretes a corresponding hormone and acts on other endocrine organs or glands in the body. There are many types of pituitary adenomas, but they can be divided into two main groups: hypersecreting pituitary tumors and non-hypersecreting pituitary tumors. Hypersecretory pituitary tumors are pituitary tumors that arise from hormone-secreting cells. The hormone-secreting cells of the pituitary gland develop into tumors, secreting too much hormone in the blood. These hormones affect other endocrine organs or glands of the body and disrupt their functioning.
Non-secretory pituitary tumors are pituitary tumors arising from non-hormonal glandular cells. The pituitary hormone in these patients is not elevated in the blood, but is sometimes decreased. The pituitary tumor grows larger and larger, compressing the adjacent healthy pituitary cells, reducing or disrupting hormone secretion. The tumor gradually enlarges and compresses adjacent brain structures, causing compression syndrome like other intracranial tumors.
According to many studies, one in 10 adults has a pituitary tumor. But most of these pituitary tumors are very small, have no clinical symptoms or never show any signs and do not require treatment. The percentage of patients with pituitary tumors that need treatment is very low. Pituitary tumors account for 25% of surgically operated intracranial tumors.
Symptoms of pituitary gland tumor

Signs of a patient with a pituitary tumor depend heavily on the type of hormone the tumor secretes, the size, location, and extent of growth of the tumor. A growing pituitary tumor usually causes three groups of symptoms:
Signs of endocrine disorders:
+ Increased prolactin secretion causes the patient to have amenorrhea, delayed menstruation, menstrual disorders, infertility, breast milk secretion (even though not pregnant, no period). Male patients may experience decreased libido, decreased or lost erections, and impotence.
+ Increased secretion of growth hormone (GH) causes the patient to develop many other disorders such as acromegaly, large face, wide forehead, protruding forehead, wide chin, thick lips, rough skin, feet and legs. Big toes, big hands and fingers… Looking at the face of a patient with GH-secreting pituitary tumor (Acromegaly) is very special. The patient can be diagnosed immediately by observing the face.
ACTH-secreting pituitary tumor causes Cushing’s disease. Patients often have signs of weight gain, stretch marks on the abdomen, thighs, hands … flabby muscles, big belly, small limbs.
+ Signs of hypopituitarism: Non-secreting pituitary tumor compresses healthy pituitary cells, causing hypopituitarism, decreased secretion of hormones, causing signs such as impotence, infertility, hair loss, loss of appetite. fatigue, dry skin, growth retardation or delayed puberty in children… Some cases of bleeding in pituitary adenomas can cause signs of acute hypopituitarism with signs of hypopituitarism appearing quickly, severe headaches. severe headache, rapid blurred vision. Hypopituitarism due to bleeding pituitary tumor is a neurosurgery emergency that requires prompt, correct and timely management.
+ Signs of visual disturbances: The pituitary tumor is located right in the pituitary fossa, below the optic nerve (where the two optic nerves cross), so when the tumor is large, it compresses, causing visual disturbances such as blurred vision, semi-fragile (only one can see inside or outside). With hemiparesis, the patient can only see images in front of the face, cannot see objects outside of the temple (temporal hemiparesis), or cannot see objects inside (nasal hemisphere). Some patients notice signs of semi-fragility, some are only discovered by the doctor during examination. Tumor invades to the side (into the cavernous sinus) causing strabismus, double vision, facial numbness, etc., due to compression of nerves III, IV, and V.
+ Signs of tumor compression causing increased pressure in the skull: Tumor compressing in the skull causes increased pressure in the skull such as headache, vomiting, nausea, confusion… even coma.
at Blogtuan.info – Source: dantri.com.vn – Read the original article here