Is “pumping” more than 22 billion USD enough?
Few companies spend more percent of their revenue on Research and Development (R&D) than Huawei Technologies Co, which sees the development of new technology as an issue to stave off trade and investment sanctions. of the United States. Accordingly, China’s largest technology giant almost doubled its R&D budget over the past half-decade to $22.1 billion by 2021.
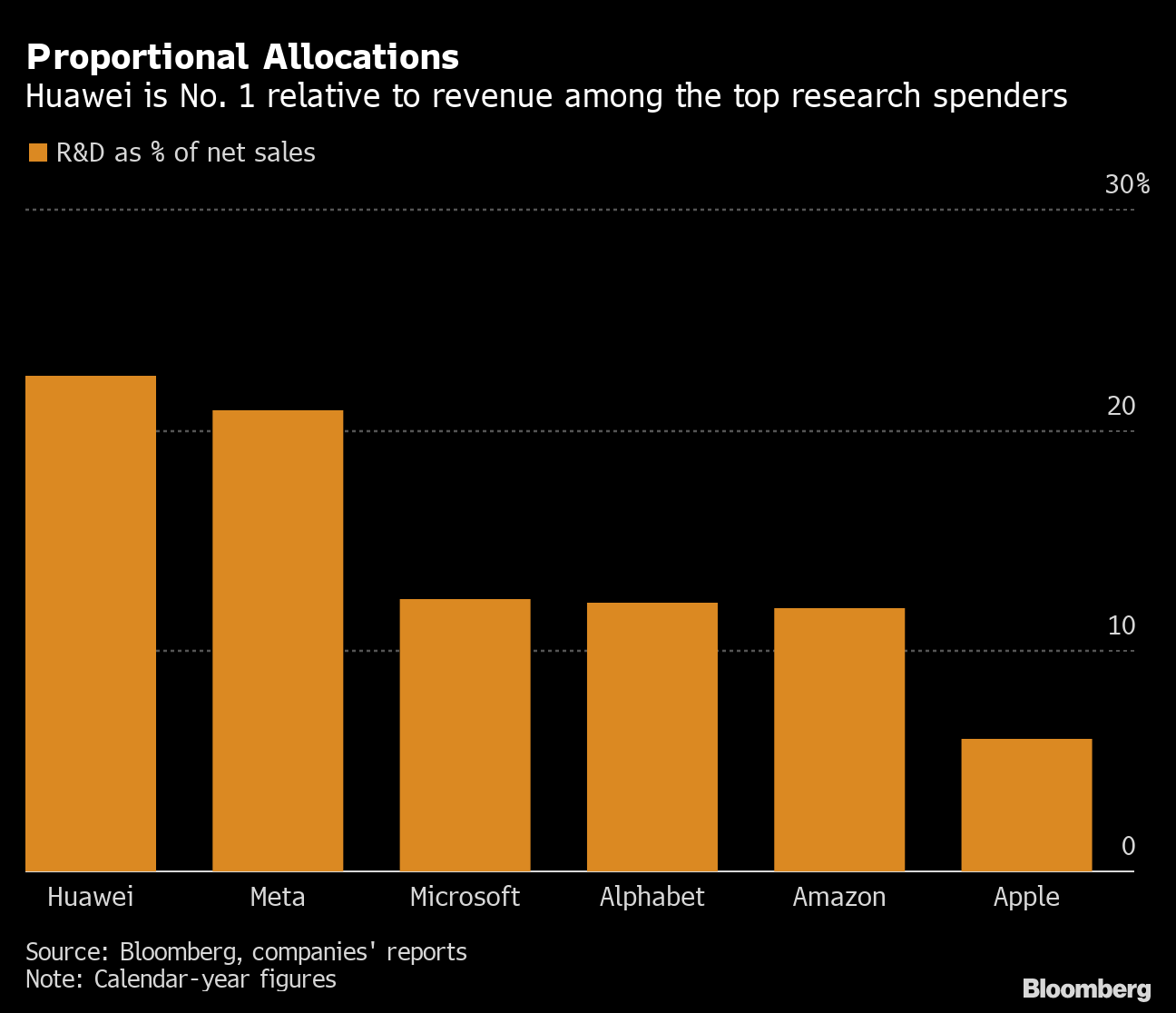
Huawei ranks first among companies that spend heavily on Research and Development (R&D) as a percentage of revenue. Photo: @AFP.
As a percentage of R&D investment as a percentage of total revenue, this represented 22.4% of the company’s revenue that year: almost twice Amazon’s share. .com Inc and Alphabet, owner of Google and more than tripling of iPhone maker Apple Inc. Only Meta Platforms Inc followed closely behind with 20.9%, data compiled by Bloomberg showed.
In terms of actual budgets, according to Bloomberg data, Huawei is one of only six companies worldwide that spent more than $20 billion on R&D last year. The total amount of money Huawei spends on R&D is almost equal to Microsoft, about 1 billion USD less than Apple and 2.5 billion USD less than Meta (Facebook’s parent company). Meanwhile, Amazon and Alphabet top the list with total expenditures of $56 billion and $32.6 billion, respectively, on R&D.
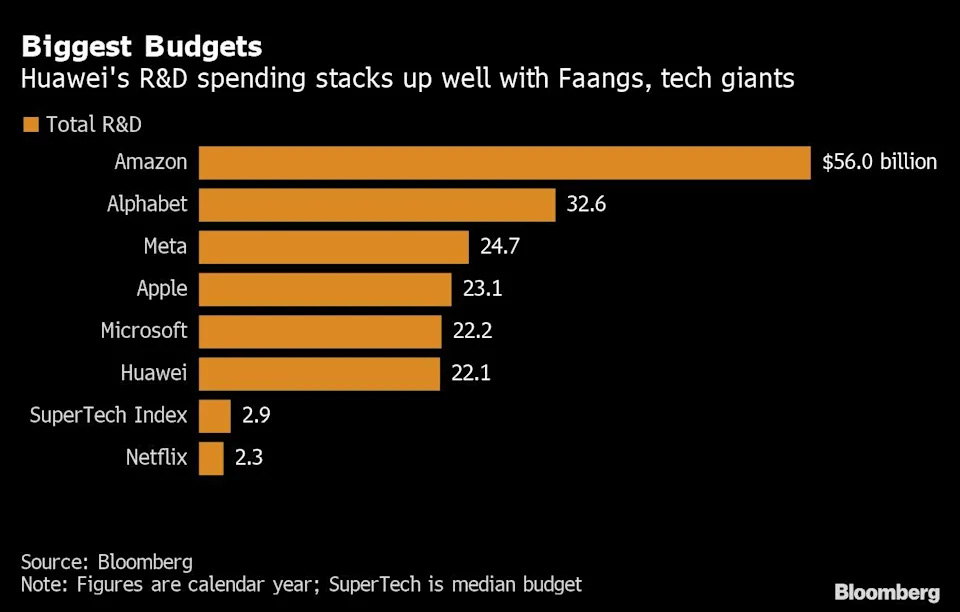
Huawei’s R&D spending is almost on par with Microsoft’s, about $1 billion less than Apple and $2.5 billion less than Meta (Facebook’s parent company). Photo: @AFP.
That increase underscores Huawei’s steady efforts to develop chips, networking gear and even smartphones that don’t use US technology, which has been banned since 2019 after Washington accused Huawei of endangering Huawei. danger to the national security of the United States. Far-reaching sanctions have wiped out nearly a third of revenue in 2021, helping to boost the share Chinese companies spend on Research and Development (R&D).
While sanctions imposed during Donald Trump’s presidency have hurt its smartphone business and restricted its 5G equipment in parts of Europe and Asia, the The company sought to raise capital by selling off assets and relying on its industry-leading IP portfolio. In 2021, Huawei sold its Honor phone unit to a state-led consortium, and scrapped its x86 server business to another Chinese consortium.
The Chinese company said it has 195,000 employees in 2021, of which 107,000 – 55% – “work in R&D”. Guo Ping, Huawei’s former rotating chairman and now chairman of Huawei’s supervisory board, told reporters during a press conference: “The problems facing Huawei today cannot be solved by cutting costs. Huawei can’t have advanced technologies, we have to increase investment in technology development.”
“It is not a matter for us to survive as a company, but whether we can keep our leading position. We will not be able to lead the world in 3- Next five years if we can’t develop our own technology.” Guo Ping said.
“Huawei’s ability to ‘survive and grow’ depends on continued investment in development. Our battle to survive is not over yet,” Guo said. “No matter what comes our way, we will continue to invest. It’s the only way forward.”
“We will continue to invest heavily in R&D,” Huawei said in a press statement.

Rising R&D costs demonstrate Huawei’s determination to survive at all costs by developing chips, networking equipment and even smartphones amid US technology-free sanctions. Photo: Photo: @AFP.
Furthermore, for Huawei, investment is not only for R&D, but also for incubating ICT Talents.
“Seeds for the Future” is Huawei’s global corporate social responsibility (CSR) flagship program. Launched in 2008, the program aims to “develop local ICT talent, enhance knowledge transfer, help participants better understand the ICT sector, and stimulate their interest.” for the field, while promoting and encouraging participation in building digital communities.
In addition, Huawei ICT Academy, another global non-profit program, acts as a bridge between companies and colleges, helping to build a talent ecosystem for the IT industry- TT. Huawei has cooperated with nearly 60 Philippine universities and established ICT academies; More than 9,000 students participate in this program.
By the end of 2021, Huawei has awarded more than 550,000 certifications worldwide, of which more than 17,000 are specific to Huawei Certified IT Professionals (HCIEs). Last year, Huawei also launched the HCIE 100 project in the Philippines. Engineers who pass these certifications will be a valuable resource for the industrial digitalized world.
Over the past five years, Huawei has also taken a big lead over other Chinese companies in terms of patents granted. Followed by OPPO, BOE, State Grid and TSMC, according to PatSnap, a third-party patent consulting firm.
at Blogtuan.info – Source: danviet.vn – Read the original article here